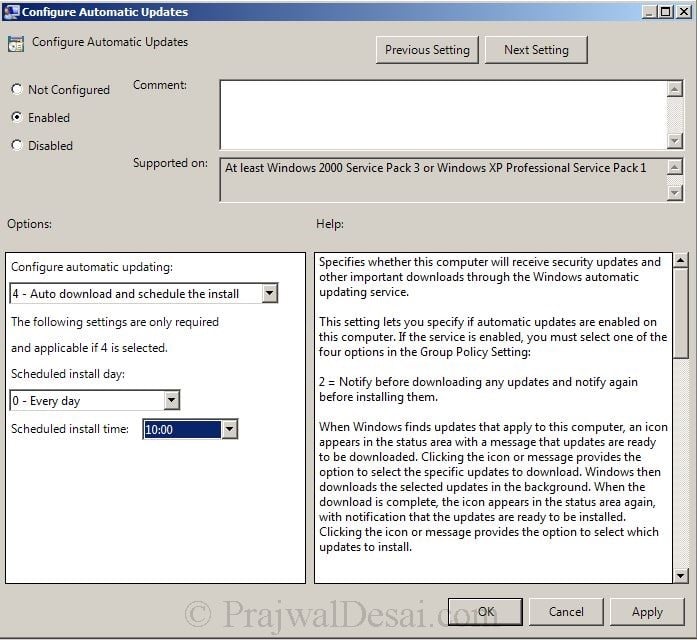
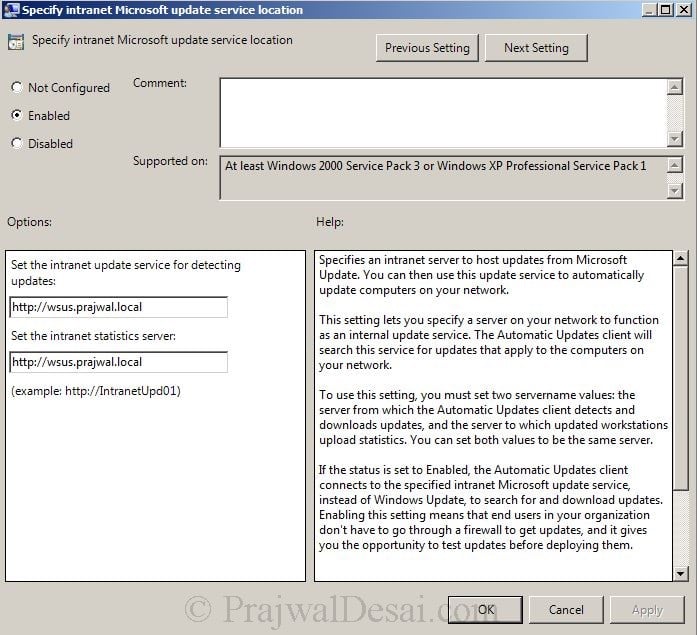
Most Useful ESXCLI and ESXi Shell Commands for Your VMware Environment
VMware provides a powerful and convenient graphical interface for managing ESXi servers – you can use a VMware vSphere Client that is a standalone application on Windows machines for managing ESXi hosts and the entire vSphere environment. Another option is to use VMware vSphere Web/HTML5 Client on any machine. Thus, you can launch a web browser for managing vSphere with ESXi hosts and VMware Host Client for managing ESXi hosts in a web browser.
The majority of settings are available in the graphical user interface (GUI), though sometimes you may need to get some information or change a configuration that is not displayed in the GUI. In this case, using the command line interface (CLI) is what you need – it is possible to configure all settings, including the hidden ones in the command line, which is also referred to as the console. In addition to traditional commands that are the same in Linux and ESXi, ESXi has its own ESXCLI commands. The most useful ESXCLI commands are explained in today’s blog post. This blog post has been created in the format of a catalog which lists useful ESXCLI commands that are part of the ESXi shell commands.
How Do I Open the CLI in ESXi?
By default, ESXi shell is disabled for local and remote access; hence, you are not able to run ESXi shell commands until you enable the ESXi shell. VMware has made this restriction for security reasons. There are three main methods for enabling the command line interface in ESXi.
Using the ESXi default interface
In the ESXi Direct Console User Interface (DCUI), go to Troubleshooting Options, navigate to Enable ESXi Shell and Enable SSH strings and press Enter to enable each option. After enabling the ESXi shell, press Alt+F1 to open the console on the machine running ESXi. You should enter your login and password after that (credentials of the root user can be used). If you need to go back to the ESXi DCUI, press Alt+F2. The Enable SSH option allows you to open the ESXi console remotely by using an SSH client.

Using VMware Host Client
Open a web browser and enter the IP address of your ESXi host in the address bar, then log in. Go to Host > Actions > Services and click Enable Secure Shell (SSH). Now you can connect to the ESXi console by using your SSH client remotely. Similarly, you can enable the console shell on a local ESXi host in the Services menu.
Using vCenter and VMware vSphere Client
This method can be used if your ESXi host is managed by vCenter Server. In VMware HTML5 vSphere Client, go to Hosts and Clusters, select your ESXi host, select the Configure tab, open System > Services and click SSH in the list of services. After that, hit Start to launch the SSH server once, or hit Edit Startup Policy and select Start and Stop with host if you wish to enable the SSH server for an extended period of time. You can also enable the ESXi shell in the Services menu.

In order to connect to the ESXi console remotely via SSH, in the Linux console, type a command like ssh 192.168.101.221, where 192.168.101.221 is the IP address of the ESXi server used in this example. You need to enter the login and password of the ESXi user in this case (root can be used by default).

In Windows, you can use PuTTY as an SSH client for running ESXI shell commands remotely.

About ESXCLI Commands
ESXCLI is a part of the ESXi shell, this is a CLI framework intended to manage a virtual infrastructure (ESXi components such as hardware, network, storage, etc.) and control ESXi itself on the low level. All ESXCLI commands must be run in the ESXi shell (console). Generally, ESXCLI is the command that has a wide list of subcommands called namespaces and their options. The ESXCLI command is present right after ESXi installation along with other ESXi shell commands. You can locate ESXCLI and explore the nature of ESXCLI after executing the following commands:
which esxcli
ls -l /sbin/esxcli

As you see in the console output, ESXCLI is a script written in Python that is located in the /sbin/ directory. If you want to see the contents of the script, you can use the built-in text editor vi.
Thus, ESXCLI consists of branches that are the main categories (namespaces) of ESXCLI commands. Notice that ESXCLI commands are case-sensitive, similarly to other console commands used in ESXi. The entire list of all available ESXCLI namespaces and commands is displayed after running the command:
esxcli esxcli command list
The list of available ESXCLI commands depends on the ESXi version.
Hence, the list of top ESXCLI namespaces for ESXi 6.7 is as follows:
- device – device manager commands
- esxcli – commands related to ESXCLI itself
- fcoe – Fibre Channel over Ethernet commands
- graphics – VMware graphics commands
- hardware – commands for checking hardware properties and configuring hardware
- iscsi – VMware iSCSI commands
- network – this namespace includes a wide range of commands for managing general host network settings (such as the IP address, DNS settings of an ESXi host, firewall) and virtual networking components such as vSwitch, portgroups etc.
- nvme – managing extensions for VMware NVMe driver
- rdma – commands for managing the remote direct memory access protocol stack
- sched – commands used for configuring scheduling and VMkernel system properties
- software – managing ESXi software images and packages for ESXi
- storage – commands used to manage storage
- system – commands for configuring VMkernel system properties, the kernel core system and system services
- vm – some commands that can be used to control virtual machine operations
- vsan – VMware vSAN commands
The main commands appear as verbs indicating the same action:
- list – show the list of objects available for the defined namespace (for example, esxcli hardware bootdevice list – list available boot devices)
- get – get the value of the defined setting or property (for instance, esxcli hardware clock get – check the time set)
- set – set the necessary parameter manually (for example, esxcli hardware clock set -y 2019 -s 00 – set the year to 2019 and set the seconds to 00)
- load/unload – load/unload system configuration (esxcli network firewall load – load the firewall module and firewall settings stored in the configuration file)
If you are unable to remember a particular ESXCLI command related to the appropriate namespace, you can enter the command and see a tip in the output of the console—for example, type:
esxcli network to see all available commands for the network namespace, then type:
esxcli network vm to check the commands for the vm namespace.

The ESXCLI log file is located in /var/log/esxcli.log
The data is written to this file if an ESXCLI command has not been executed successfully. If an ESXCLI command is run successfully, nothing is written to this log file.
Useful ESXCLI Commands
Now that you are familiar with the basic working principle of ESXCLI commands, let’s consider the particular examples of useful ESXCLI commands which can be used in VMware vSphere. The list of ESXCLI commands considered in this article is divided by categories equivalent to namespace names.
Checking hardware
By using the hardware namespace, you can view the full information about installed devices. In order to view installed PCI devices, run the following ESXCLI command:
esxcli hardware pci list | more
Check the amount of memory installed on the ESXi server:
esxcli hardware memory get

View the detailed information about installed processors:
esxcli hardware cpu list
System settings
In this section, you can see the commands of the system esxcli namespace.
Check the precise ESXi version and build number, including the number of installed updated and patches:
esxcli system version get
Check the hostname of an ESXi server:
esxcli system hostname get
Check the ESXi installation time:
esxcli system stats installtime get

Check the SNMP configuration:
esxcli system snmp get
Enter the ESXi host to the maintenance mode:
esxcli system maintenanceMode set --enable yes
Exit the maintenance mode:
esxcli system maintenanceMode set --enable no
After entering an ESXi host to the maintenance mode, you can shut down or reboot the host.
Power off an ESXi host:
esxcli system shutdown poweroff
The command for rebooting the host is similar:
esxcli system shutdown reboot
You can also set a delay and write a reason of rebooting the host to be saved in system logs:
esxcli system shutdown reboot -d 60 -r “Installing patches”
In this example, the delay is 60 seconds.
Another command is to set the custom welcome message instead of a standard background screen with a shaded inactive main menu where the “<F2> Customize System/View Logs <F12> Shut Down/Restart” tip and the IP address to manage the host are displayed. Notice that after setting a custom welcome message you will see only this set message on the black screen. You can type “Press F2” manually to avoid confusion. The custom message can be used for hiding information about your ESXi host on the display connected to the ESXi host when a user is not logged in.
esxcli system welcomemsg set -m="Welcome to NAKIVO! Press F2"
Verify whether the welcome message is already set:
esxcli system welcomemsg get

Network settings
The network namespace is one of the largest namespaces of ESXCLI. Let’s explore the commands that can be useful for diagnostics.
Check the status of active network connections:
esxcli network ip connection list

View the list of installed network adapters:
esxcli network nic list

Display the information about network interfaces:
esxcli network ip interface list
Display the information about IP addresses of the network interfaces that are present on the server:
esxcli network ip interface ipv4 get
Display the network information for VMs:
esxcli network vm list

View the domain search settings:
esxcli network ip dns search list
View the DNS servers set in the network settings:
esxcli network ip dns server list
List virtual switches and port groups:
esxcli network vswitch standard list
Show statistics for the vmnic0 network interface:
esxcli network nic stats get -n vmnic0
Check the firewall status and rule settings:
esxcli network firewall get
esxcli network firewall ruleset list
Note: The default firewall policy is to drop traffic if the opposite rules are not set.
You can temporary disable the firewall on an ESXi host for troubleshooting:
esxcli network firewall set --enabled false
The firewall must be enabled with the command:
esxcli network firewall set --enabled true
It is recommended to have the ESXi firewall enabled for security reasons.
The network namespace includes many commands. Only basic and the most popular of them are considered in the Network section of today’s blog post. It is possible to configure a high number of network parameters with esxcli, but would require a long walkthrough that is out of scope for today’s article.
Storage
The storage namespace allows you to check and edit storage settings.
Check the information about mounted VMFS volumes:
esxcli storage vmfs extent list
View mappings of VMFS file systems to disk devices:
esxcli storage filesystem list
List all the iSCSI paths on the system:
esxcli storage core path list
Display the list of mounted NFS shares:
esxcli storage nfs list
How do you check SMART with esxcli? S.M.A.R.T. is useful for disk diagnostics and for preventing disk failure. You can read the S.M.A.R.T. data and, if you discover that something is wrong with your disk, you can make a timely decision to replace the disk.
First, list all storage devices and locate the unique device name (see the screenshot below):
esxcli storage core device list
Then, use the command to get the S.M.A.R.T. data of that disk device:
esxcli storage core device smart get -d naa.50026b7267020435
where naa.50026b7267020435 is the name of the device used in this example.

iSCSI
iSCSI is a widely used protocol for accessing shared storage on a block level, and there is a separate iscsi namespace in ESXCLI for managing the iSCSI storage.
Show the list of available iSCSI adapters:
esxcli iscsi adapter list
Re-discover and re-scan iSCSI adapters:
esxcli iscsi adapter discovery rediscover -A adapter_name
esxcli storage core adapter rescan -A adapter_name
Instead of -A adapter_name you can rescan all adapters by using the --all option.

Software
Software packages intended for ESXi are usually distributed as VIB files (vSphere installation bundle). A VIB file is similar to a container with zipped packages that can be installed in the system, with a descriptor and a signature file. In turn, VIBs are usually distributed as files packed into an archive file in the standard ZIP format. You may need to include VIBs into an ESXi image in order to use the appropriate hardware or install VIBs in an existing system for applying a security patch.
You can view the list of VIB packages installed on your ESXi host:
esxcli software vib list
You can install a VIB with ESXCLI (the ESXi host must be in maintenance mode):
esxcli software vib install -d /vmfs/volumes/datastore1/patches/patch_name.zip
VM operations
The vm namespace can be used for operations on running virtual machines processes.
Check the list of running VMs and display their World IDs:
esxcli vm process list

You can kill the unresponsive virtual machine with ESXi shell commands. Using ESXCLI, in this case, can be helpful when a VM cannot be shut down via GUI, such as the GUI of VMware vSphere Client, VMware Host Client or VMware Workstation.
Shut down the VM by using the World ID displayed in the output of the esxcli vm process list command. In the current example, the World ID of the necessary VM is 75498.
esxcli vm process kill -w 75498 -t soft
If the soft command type was not helpful, consider performing an immediate shut down of the VM by using the hard method.
esxcli vm process kill -w 75498 -t hard
There are three available command options for the kill command:
soft - a correct signal is sent in the guest operating system to shut down a VM correctly;
hard - a VM is shut down immediately;
force - VM is powered off similarly to how a computer is powered off when unplugging the power cable. Only use this type of powering off the VM if the previous two types were unsuccessful.
Other Useful ESXi Shell Commands
Besides ESXCLI commands, you can use a lot of ESXi shell commands. The ESXi shell commands list that may be useful for you is provided below.
Open the ESXi DCUI from the console (the colors are different when you connect to the ESXi shell via SSH):
dcui

Press Ctrl+C to go back to the command prompt.
Convert a thick provisioned virtual disk to a thin provisioned virtual disk by using vmkfstools:
vmkfstools -i /vmfs/volumes/vmfs_datastore/vm_name/thick_disk.vmdk -d thin /vmfs/volumes/vmfs_datastore/vm_name/new_thin_disk_name.vmdk
Among ESXi shell commands, vmkfstools is a powerful command for performing storage operations as well as managing storage devices, VMFS volumes, and virtual disks. Read more about thick and thin provisioning as well as virtual disk shrinking in the blog post.
Open the ESXi task manager:
esxtop
After opening the task manager with the esxtop command, you can switch between tabs by pressing the appropriate keys:
C - CPU
I – interrupt
M – memory
N – network
D – disk adapter
U – disk device
V – disk VM
P – power management
Find the file in the current directory:
find . -name filename.txt
Replace the . character with the name of the directory in which you would like to locate a file, and replace filename.txt with your file name. For example, if you wish to find a diskname.vmdk file in the /vmfs/volumes/ directory, run the command:
find /vmfs/volumes/ -name diskname.vmdk
Open the interactive VMware console:
vsish
Show loaded vmkernel drivers:
vmkload_mod --list
Check the settings of the swap partition:
esxcli sched swap system get
You can list users by using one of the following commands:
esxcli system account list
cat /etc/passwd or less/etc/passwd

Creating a new user
There are at least two methods of creating a new ESXi user by using ESXi shell commands.
Using the adduser command
If you type the adduser command in the ESXi console, you will get the message:
-sh: adduser: not found
You should define the full path to the appropriate busybox binary to run this command:
/usr/lib/vmware/busybox/bin/busybox adduser
Now you can see the usage options for this command.
Finally, run the exact command to add an ESXi system user:
/usr/lib/vmware/busybox/bin/busybox adduser -s /bin/sh -G root -h / user1
Where:
-s /bin/sh is a shell used after user login;
-G root – the group name whose member is a new user (the root group);
-h / is a home directory (the root directory) of a new user;
user1 is the user name.
Enter a new password and confirm the password when prompted.

Using ESXCLI
As an alternative, you can add a new user just with the one command by using esxcli:
esxcli system account add -d="test user" -i="username" -p="Password-Test321" -c="Password-Test321"
Where:
-d means the displayed description
-p is the password set for the new user
-c is the password confirmation
Which method of creating a new user in the command line is better? The single command used in the second method may appear to be the optimal method for creating a new user, but it is not entirely true on account of security reasons. If you’ve been attentive, you should be able to remember the warning message displayed right after logging in to the ESXi shell:
All commands run on the ESXi shell are logged and may be included in support bundles. Do not provide passwords directly on the command line. Most tools can prompt for secrets or accept them from standard input.
If security is a concern for you, enter commands without including passwords as plain text into the commands. If a password is needed, it is usually prompted and can be entered in the standard console input. For example, if you would likr to create a new user with ESXCLI, use a command like:
esxcli system account add -d="user2" -i="user2" -p -c
A password will be prompted separately and will not be displayed in the console while entering the password.

Conclusion
Today’s blog post has covered a series of ESXi shell commands including ESXCLI commands. Using the command line interface in ESXi gives you more power in addition to nice graphical user interfaces of VMware vSphere Client and VMware Host Client for managing ESXi hosts. You can use ESXi shell commands for viewing and configuring settings that are hidden or not available in the GUI. Use the ESXi shell commands list provided in this blog post for fine ESXi tuning and experience the extra power of using the command line interface in VMware vSphere. You can learn more by reading about PowerCLI, another type of the command line interface for managing VMware vSphere from Windows PowerShell.